Patents
|
Localization of Planar Objects in Images Bearing Repetitive Patterns.
Luis Baumela Molina, José Miguel Buenaposada Biencinto, Roberto Valle Fernández, Miguel Ángel Orellana Sanz, Jorge Remirez Miguel
US Patent
US 10922582 B2
,
Eropean Patent
EP 3465531 B1
Priority 2016
|
|
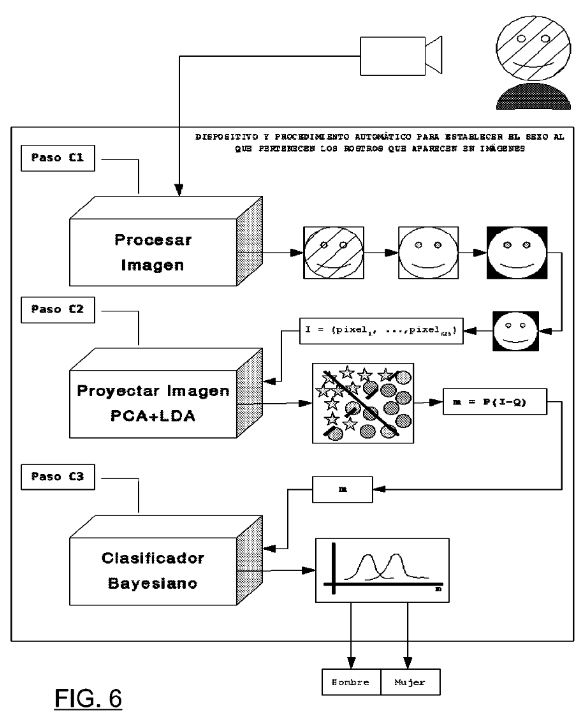
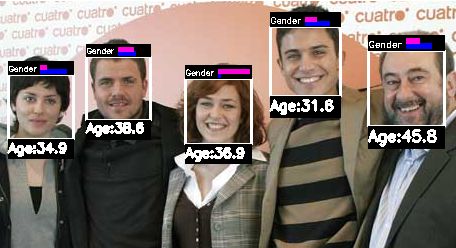
Device and automatic procedure for establishing the sex of faces appearing in images.
Juan Bekios Calfa, Luis Baumela Molina, José Miguel Buenaposada Biencinto
Spanish patent ES 2339100 B2.
Priority 2010
|
Facial Atributes
|
Dependencies between facial attributes given the appearance.
Recent works report significant drops in performance for state-of-the-art
gender classifiers when evaluated "in the wild", i.e. with uncontrolled
demography and environmental conditions. By considering the relation
between gender and pose attributes we also avoid the use of computation-ally expensive
and fragile face alignment procedures. In the experiments we confirm the existence
of dependencies among gender, age and pose facial attributes and prove that we can
improve the performance and robustness of gender classifiers by exploiting these
dependencies.
|
|
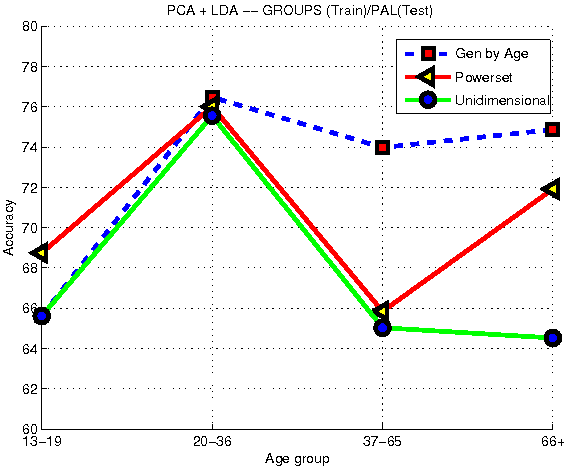
Facial age estimation .
We developed a "light weight" face age estimation algorithm using PCA+LDA and KNN regression.
Related Publications:
IBPRIA'2011,
|
|
PCA+LDA face gender recognition.
We developed gender classification algorithm using an
simple holistic approach. We got 93% accuracy on FERET database (5-fold cross validation) and
an speed comparable to the fastest gender recognition algorithms. This algorithm is
based on PCA+LDA with proper cross-validation of PCA dimensions.
Related Publications:
PAMI'2011,
Some videos:
[Video 1 (youtube)]
[Video 2 (vimeo with sound)]
|
|
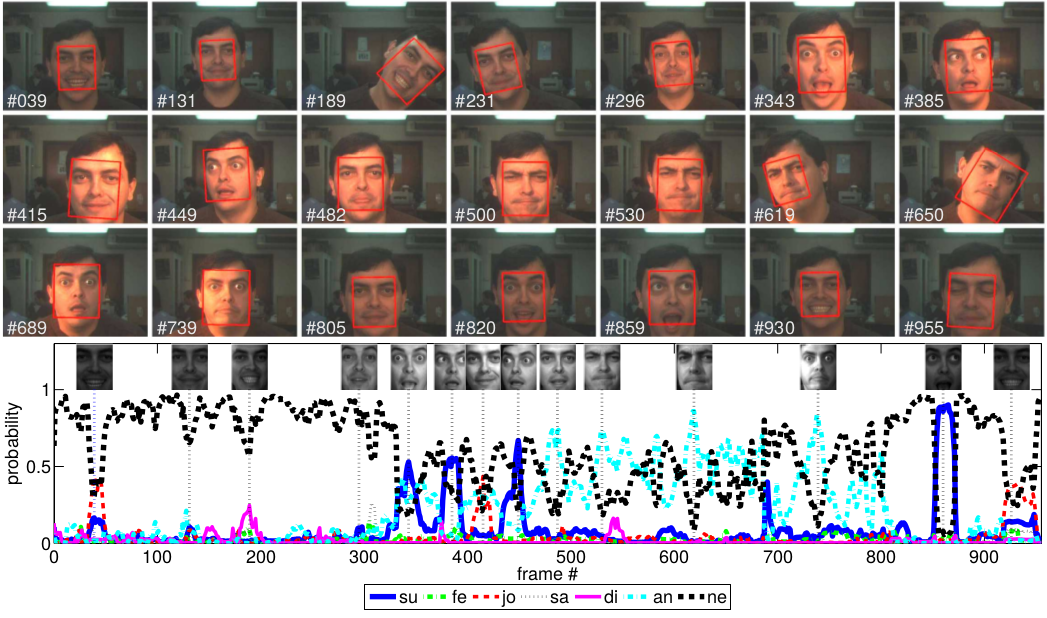
Face expressions recognition.
We used our 2D appearance tracking algorithm [BMVC'2006]
to track the face. We developed a user independent manifold of face expressions using PCA+LDA and then
we classified the expressions using KNN.
Some videos:
[Video 1 (youtube)]
[Video 2 (mpeg)]
Matlab scripts: Cohn-Kanade database a priori classification of facial expresions |
Machine Learning
|
Multiclass cost-sensitive boosting: BAdaCost.
We introduce a cost-sensitive multi-class Boosting algorithm (BAdaCost) based on a generalization
of the Boosting margin, termed multi-class cost-sensitive margin. It can be used, for example, to
address the class imbalance by the introduction of a cost matrix that weighs more hevily the costs
of confused classes. Other interesting uses are multi-view object detection.
Related Publications:
IBPRIA'2015
PR'2018
|
Tracking
|
Speeding-up homography estimation in mobile devices.
We introduce a procedure for reducing the number of samples required for
fitting a homography to a set of noisy correspondences using a random
sampling method. This is achieved by means of a geometric constraint that
detects invalid minimal sets.
Related Publications:
JRTIP'2015,
|
|
Efficient 3d nonrigid tracking. Efficient incremental image alignment is a topic of renewed interest in the computer
vision community because of its applications in model fitting and model-based object
tracking. We are working in efficient solutions to the 3D tracking of a head performing
face expressions under changing illumination conditions.
|
|
|
Efficient appearance-based tracking with illumination changes and face expressions.
separates facial expressions from illumination variations. The
appearance of a face is represented by the addition of two
independent linear subspaces modelling facial expressions and
illumination. This simple model enables us to train the system with
no manual intervention. We also introduce an efficient procedure
for fitting this model, which can be used for tracking a human face
in real-time.
Some videos:
[Video 1],
[Video 2],
[Video 3],
[Video 4]
You can download the original sequences used in our tests (BMVC 2006 paper image sequences). |
|
Efficient appearance-based tracking
We have developed an efficient way of minimizing the
eigentracking
for nonrigid motion estimation. It is based on the precomputation of motion templates to save
on-line computation. It allows as to estimate appearance (PCA coefficients) and motion in real-time.
Related Publications:
ANM'2004
Some videos:
[Video 1]
|
|
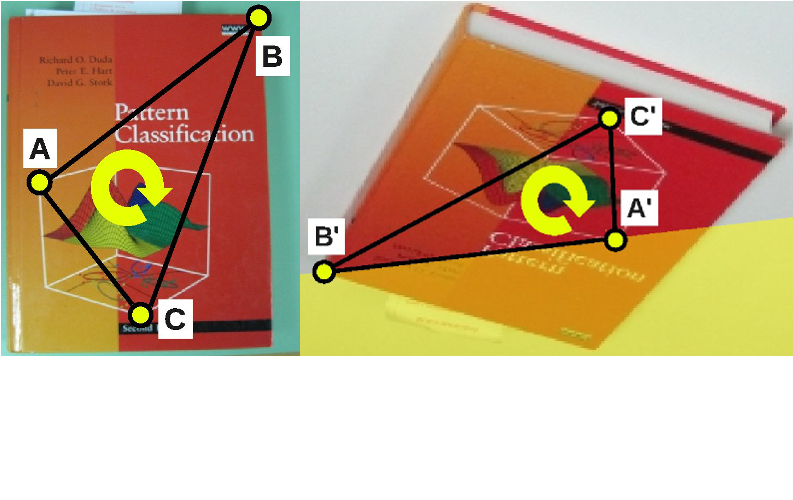
SSD based 3D tracking.
We have developed an algorithm for tracking a
rigid object based on a piecewise planar model. The tracking is
performed using a single incremental SSD-based tracker. The main
feature of the approach presented is that it can track a rigid set of
arbitrarily small patches all of which could not be individually tracked.
Related Publications:
IbPRIA'2003,
VLBV'2003
|
|
SSD based tracking.
Planar tracking can be used for face tracking. We have
extended a well known framework for planar tracking
(see [Hager98])
with a projective motion model. Additionally, using a calibrated camera, it is
possible to estimate the 3D pose of the planar object. We have also developed
a procedure to select the most informative pixels of the target template
image for faster tracking.
|
|
Colour Based Tracking.
Tracking using colour is difficult when sudden light colour changes
take place. We have extented a well known colour constancy
algorithm, Grey World, to deal with such situations.
The result is more robust than widely used RGB-normalisation,
although it is not perfect either.
|
|
Robust face tracking.
All the algorithms based on a simple visual cues fail in some
circumstances. The key idea is to use this simple algorithms
together in order to get robustness. All this algorithms should be
"orthogonal" in the sense of having different fail conditions.
Related Publications:
CAEPIA'1999
Some videos (mpeg):
Colour and SSD tracking
|
Commercial
|
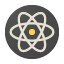
Building Facade Localization.
We developed new algorithms for real-time planar building facades localization.
This is not an easy problem given the repetitive structures in the building
texture. Work funded by The Graffer.
Our algorithms, implemented by the Computer Vision engineers at The Graffter,
are able to run at 6-10 fps in a Google Nexus 5 on Android.
|
|
OCR for ID documents on video.
We developed and implemented our own algorithms for the OCR of spanish ID documents. The
funding came from Work funded by CAB Magazine Online S.L. (an Spanish company).
The goal of the project was to read the 3 OCR lines of the spanish ID documents in short videos. Other countries have only 2 OCR lines. Our software is valid for this other documents also with minimal customization. In this project we developed a full prototype using C++ and OpenCV on GNU/Linux. The prototype is fully functional (10 fps on an Intel Core i5). It makes one mistake on average per ID document (in our limited test cases of few IDs). Unfortunately the company gave up on the project before the full validation of the prototype so we have the software and the project available to any interested company :-)
Videos:
[Video1]
|
|
Facial analysis for video analythics.
We developed a set of low computational requirements face analysis algorithms for,
Visión Artificial Desarrollos de I+D,
an Spanish company. The algorithms were integrated in a product called vAudience for Digital Signage audience
measurement.
|